Operating in Water-Stressed Regions
Ford has been growing in many areas of the world where water access and availability are a concern. We have identified which of our operations are located in water-stressed regions using data from the World Resources Institute’s EarthTrends project. Water-stressed regions are considered to be those with a per capita water supply of less than 1,700 cubic meters per year. According to our analysis, about 10 percent of our operations are located in regions that are considered to be at risk.
Our facilities in Mexico are located in water-stressed regions; our manufacturing facility in Cuautitl?n, Mexico, for example, is already subject to water-withdrawal limitations. Several of our facilities in our Asia Pacific and Africa region are in areas that are currently water-stressed, or are expected to be in the near future.
Ford Operations: 2025 Projected Annual Renewable Water Supply per Person
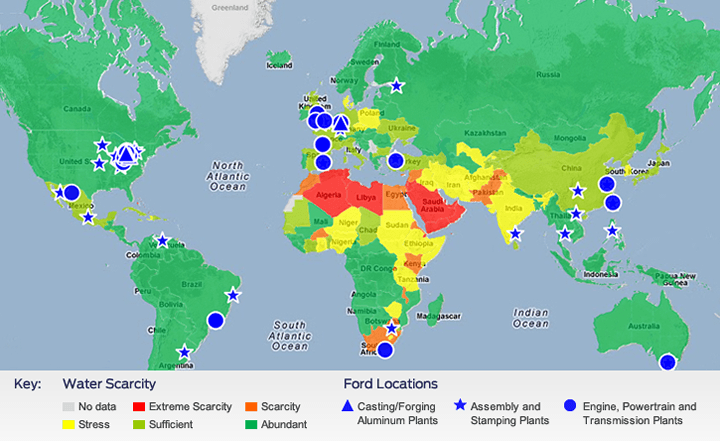
Ford used the Global Water Tool developed by the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD) to evaluate which of our operations are projected to be in water-scarce regions by 2025. According to the analysis, approximately 26 percent of our operations are projected to be in such regions (defined as areas of extreme scarcity or scarcity). The WBCSD’s free tool enables companies to map their water use and assess water-related risks. For more information on the tool and how it works, see the WBCSD website.
Sources: World Business Council for Sustainable Development’s Global Water Tool (GWT) v2. GWTv2 uses the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations AQUASTAT dataset.










