Vehicle Safety
Data On This Page
- Percent of Nameplates Achieving 3-star or Better in Rollover NCAP
- Percent of Nameplates Achieving 4-star/4-star Frontal NCAP or Better
- Percent of Nameplates Achieving 5-star/5-star Frontal NCAP
- Percent of Namplates Achieving 4-star/4-star or Better in LINCAP
- Percent of Nameplates Achieving 5-star/5-star or Better LINCAP
- IIHS Frontal Offset – Percent of Nameplates Achieving "Good" Rating
- Number of IIHS Top Safety Picks by Manufacturer
- Euro NCAP Results 2006–8
- U.S. Safety Recalls
A. Percent of Nameplates Achieving 3-star or Better in Rollover NCAP
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ford | 100 | 96 | 96 |
| Toyota | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| GM | 100 | 100 | 100 |
- Third party rated (NHTSA)
B. Percent of Nameplates Achieving 4-star/4-star Frontal NCAP or Better
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ford | 100 | 100 | 95 |
| Toyota | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| GM | 83 | 92 | 96 |
- Third party rated (NHTSA)
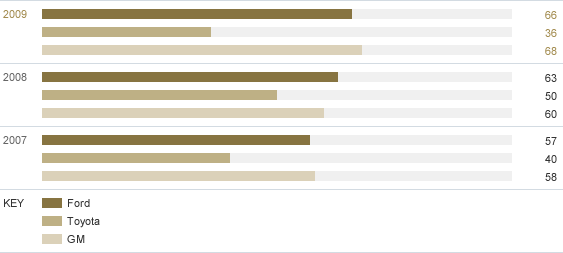
C. Percent of Nameplates Achieving 5-star/5-star Frontal NCAP
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ford | 57 | 63 | 66 |
| Toyota | 40 | 50 | 36 |
| GM | 58 | 60 | 68 |
- Third party rated (NHTSA)
D. Percent of Nameplates Achieving 4-star/4-star or Better in LINCAP
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ford | 92 | 100 | 97 |
| Toyota | 87 | 90 | 93 |
| GM | 90 | 91 | 93 |
- Third party rated (NHTSA)
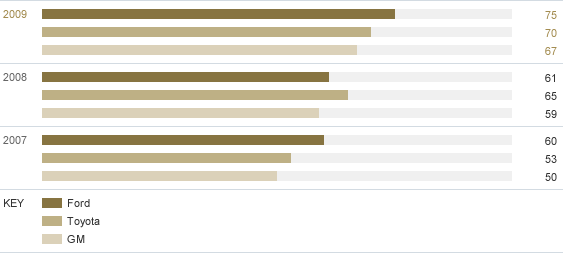
E. Percent of Nameplates Achieving 5-star/5-star or Better LINCAP
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ford | 60 | 61 | 75 |
| Toyota | 53 | 65 | 70 |
| GM | 50 | 59 | 67 |
- Third party rated (NHTSA)
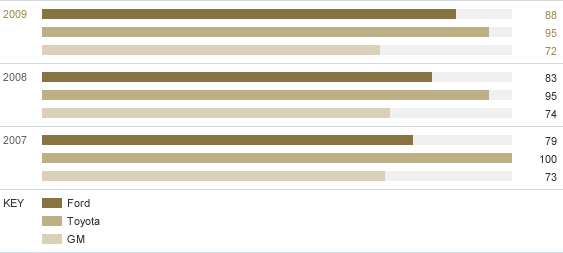
F. IIHS Frontal Offset – Percent of Nameplates Achieving "Good" Rating
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ford | 79 | 83 | 88 |
| Toyota | 100 | 95 | 95 |
| GM | 73 | 74 | 72 |
- Third party rated (IIHS)
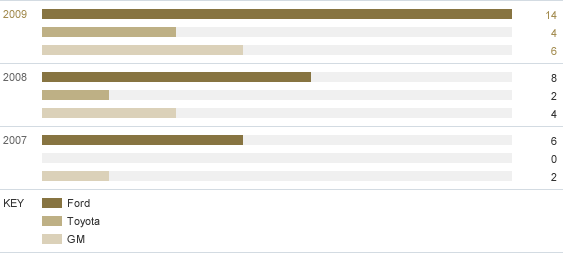
G. Number of IIHS Top Safety Picks by Manufacturer
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ford | 6 | 8 | 14 |
| Toyota | 0 | 2 | 4 |
| GM | 2 | 4 | 6 |
- Third party rated (IIHS)
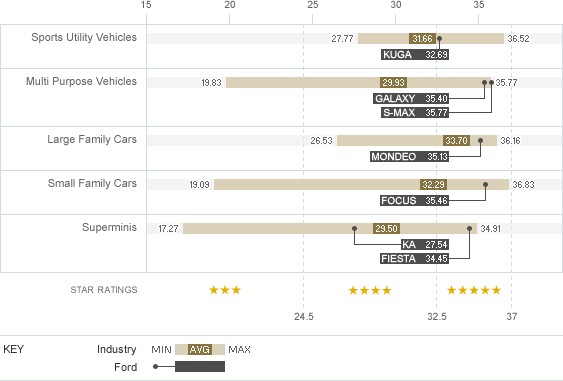
H. Euro NCAP Results 2006–8
| Industry Low | Industry High | Industry Average | Ford results | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sports Utility Vehicles | 27.77 | 36.52 | 31.66 | Ford Kuga: 32.69 |
| Multi Purpose Vehicles | 19.93 | 35.77 | 29.93 | Ford Galaxy: 35.40, Ford S-MAX: 35.77 |
| Large Family Cars | 26.53 | 36.16 | 33.7 | Ford Mondeo: 35.13 |
| Small Family Cars | 19.09 | 36.83 | 32.29 | Ford Focus: 35.46 |
| Superminis | 17.27 | 34.91 | 29.50 | Ford Ka: 27.54, Ford Fiesta: 34.45 |
- Third party rated (Euro NCAP)
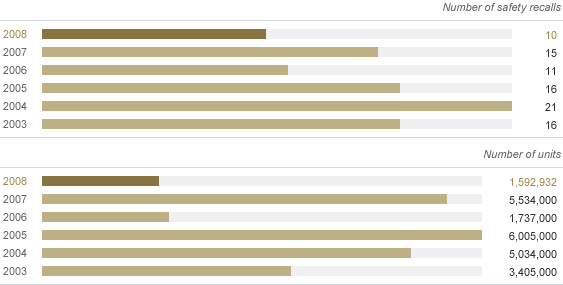
I. U.S. Safety Recalls
| 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | 21 | 16 | 11 | 15 | 10 |
| 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3,405,000 | 5,034,000 | 6,005,000 | 1,737,000 | 5,534,000 | 1,592,932 |
- Reported to regulatory authorities (NHTSA)
Notes to the Data
Chart A, Chart B, Chart C, Chart D and Chart E
U.S. New Car Assessment Program
Government star ratings are part of the New Car Assessment Program (NCAP) of the U.S. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA). In NHTSA's frontal crash rating tests, vehicles with belted front-seat test dummies are crashed into a fixed barrier at 35 mph, which is equivalent to a head-on collision between two similar vehicles, each moving at 35 mph. Since the test is designed to reflect a crash between two similar vehicles, one can meaningfully compare vehicles from the same weight class (within +/- 250 lbs) when looking at frontal crash test ratings.
Instruments measure the force of the impact to each test dummy's head, chest and legs. NHTSA uses the readings from these instruments to estimate the chance that a real occupant would sustain a serious injury in the tested frontal crash. A serious injury is defined as one that requires immediate hospitalization and may be life-threatening.
For side crash ratings, belted test dummies are placed in the driver seat and rear passenger seat (driver's side). The side crash rating is designed to represent an intersection-type collision with a 3,015 lb barrier moving at 38.5 mph into a standing vehicle. The moving barrier is covered with material that has "give" to replicate the front of a vehicle. Since all rated vehicles are impacted by the same size barrier, it is possible to compare all vehicles with each other when looking at side crash protection ratings. Instruments measure the force of impact to each dummy's head, neck, chest and pelvis. Side crash star ratings indicate the chance of a serious chest injury for the driver, front seat passenger and the rear seat passenger (first and second row occupants).
| What do the stars mean? | Chance of serious injury | |
|---|---|---|
| Frontal Crash Rating | Side Crash Rating | |
| 10 percent or less | 5 percent or less | |
| 11–20 percent | 6–10 percent | |
| 21–35 percent | 11–20 percent | |
| 36–45 percent | 21–25 percent | |
| 46 percent or greater | 26 percent or greater | |
For more information, go to www.nhtsa.dot.gov. Data are for the model year noted.
Ford believes the NHTSA rollover resistance metric is flawed as it does not include a measure of the benefits of electronic stability control systems (ESC). NHTSA's studies have shown the benefits of ESC systems and their potential to improve vehicle stability. Ford believes ESC equipped vehicles should be credited in the resistance to rollover NCAP.
Chart F
In the 40 mph offset test of the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS), 40 percent of the total width of a vehicle strikes a barrier on the driver's side. The forces in the test are similar to those involved in a frontal offset crash between two vehicles of the same weight, each going just less than 40 mph. Test results can be compared only among vehicles of similar weight. Like full-width crash test results, the results of offset tests cannot be used to compare vehicle performance across weight classes.
Based on a vehicle's performance in three areas evaluated in the frontal offset crash tested – structural performance, injury measures and restraints/dummy kinematics – the IIHS assigns a vehicle an overall crashworthiness measure of Good, Acceptable, Marginal or Poor. For more information, go to www.iihs.org.
Chart G
To earn a Top Safety Pick from the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS), a vehicle must receive a rating of "good" in offset frontal impact, side impact and rear impact evaluations, and offer electronic stability control. Top Safety Picks are the best vehicle choices for safety within size categories. 2005 (2006 Model Year) was the first year the IIHS issued Top Safety Picks.
Chart H
Adult Occupant ratings range from 0 to 5 stars. 3 star = up to 24.5, 4 star = 24.5 to 32.5, 5 star = 32.5 and above; current maximum = 37 points. For additional information, go to www.euroncap.com.
Chart I
Recalls are by calendar year rather than model year. A single recall may affect several vehicle lines and/or several model years. The same vehicle may have multiple recalls. (Source: U.S. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration.)
Related Links
- Complete ratings data by vehicle can be found on the following Web sites: